In an increasingly urbanized world, the role of nature within our communities has never been more important. The need to integrate trees and green spaces is essential not only for environmental sustainability but also for the health and well-being of residents. Community forestry, the practice of involving local communities in the management and care of community forests1, stands as a key strategy to address these needs. By fostering a close relationship between people and their natural surroundings, community forestry ensures that the many benefits of trees are recognized, valued, and preserved for future generations.
The Benefits of Trees
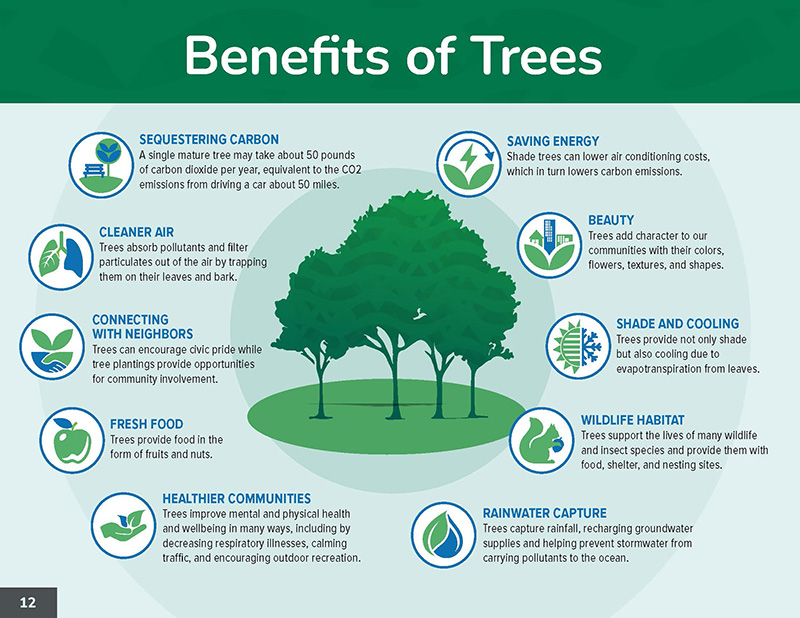
Trees are among the most valuable assets in any neighborhood, offering a wide array of environmental, social, and economic benefits that enhance the quality of life for community members. As critical infrastructure, trees help to combat climate change, improve air quality, and support biodiversity. They also offer aesthetic and recreational values, providing shade, beauty, and spaces for social interaction.
Image: A page from L.A. County's recently completed Community Forest Management Plan highlights the benefits of trees.
Given these multifaceted benefits, comprehensive planning and management of community forests are essential for sustaining the health and well-being of communities.
The Role of Community Forestry
Community forestry involves the active participation of residents, organizations, and governments in the planning, planting, and maintenance of trees. It is a collaborative approach that recognizes the importance of local knowledge and community engagement in creating and sustaining healthy community forests. Community forestry not only addresses environmental concerns but also promotes social welcoming, ensuring that all communities have access to the benefits of trees.
In urban areas, where space is often limited, community forestry programs focus on maximizing the value of every tree by carefully selecting species, locations, and management practices that best meet the needs of the community. These programs also emphasize the importance of maintaining and protecting existing trees, which are often the most valuable assets due to their size and maturity.
Community forestry can also be a powerful tool for climate adaptation. As cities face increasing challenges from climate change, such as rising temperatures, more frequent and intense storms, and prolonged droughts, community forests can provide critical resilience. Trees and green spaces help communities absorb and recover from these impacts by cooling the air, reducing flood risks, and providing shade and refuge during extreme weather events.
The Los Angeles County Community Forest Management Plan
Recognizing the importance of trees and the need for a strategic and coordinated approach to community forestry, Los Angeles County has developed the Community Forest Management Plan (CFMP or the Plan)2. This Plan represents a comprehensive strategy to enhance, expand, and sustain the county's community forest, advancing tree fairness and ensuring that everyone can enjoy the benefits of trees.

Image: The cover of L.A. County’s recently completed Community Forest Management Plan.
The CFMP enhances L.A. County’s ability to effectively manage its community forest and increase its tree canopy, especially in the communities most lacking in parks and tree coverage as identified in the Countywide Parks Needs Assessments and the CFMP, respectively. The CFMP also helps L.A. County to effectively respond to emerging threats to the community forest, such as climate change impacts and invasive pests, by setting forth consistent management approaches based on current science and identifying policy and program needs to support these approaches.
The CFMP was created by the Chief Sustainability Office (CSO) in partnership with key partners like the departments of Parks and Recreation, Public Health, and Public Works, community leaders, and L.A. County residents. This effort also involved consultation with subject matter experts and extensive community engagement and outreach conducted with the support of over twenty community-based organizations.
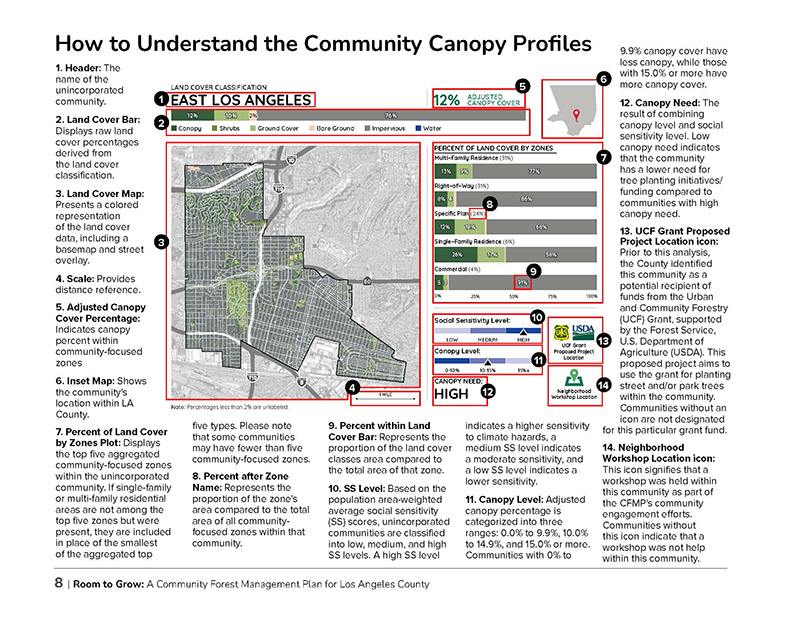
Image: A page from L.A. County's recently completed Community Forest Management Plan highlights how to understand the community canopy profiles.
According to the CFMP, the overall tree canopy cover in L.A. County is 15.9%, but trees are not equally distributed countywide. Many areas have less coverage, including East Los Angeles, the most populated unincorporated community, which has only a canopy cover of 12%. This variation is due in part to the diverse ecological conditions of the county, which span mountains, beaches, and deserts, as well as development patterns that range from highly urbanized to suburban to rural areas. But variations also result from past and present discrimination, such as in communities impacted by the legacy of redlining and other discriminatory policies and practices.
The CFMP seeks to create a more welcoming, healthy, and resilient community forest by:
- Increasing Tree Canopy Coverage: Implementation of the CFMP will increase tree planting in parks and along streets and expand tree canopy coverage, especially in underresourced communities that currently lack sufficient green spaces and trees. This is crucial for addressing environmental justice issues, as lower-income neighborhoods and communities of color often have fewer trees and are more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
- Enhancing Tree Health and Longevity: The CFMP emphasizes the importance of maintaining the health and longevity of existing trees in the county. This includes implementing best practices for tree care, such as proper pruning, watering, and pest management. By ensuring that trees are healthy and resilient, L.A. County can maximize their benefits and reduce the need for costly replacements.
- Engaging Communities: Community engagement is a cornerstone of the CFMP. The Plan highlights the importance of involving community members, local organizations, and businesses in all aspects of community forestry, from planning and planting to maintenance and stewardship. This participatory approach helps build a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents, fostering long-term support for community forestry initiatives.
- Adapting to Climate Change: The CFMP recognizes the need to adapt the county's community forest to the changing climate. This includes selecting tree species that are resilient to drought, heat, and other climate-related stresses, as well as implementing strategies to protect trees from the increasing frequency of extreme weather events.
Conclusion
Community forestry is a vital component of sustainable development, offering a wide range of benefits that contribute to the health, well-being, and resilience of communities. The CFMP represents a forward-thinking approach to community forestry, one that prioritizes access for all, sustainability, and community engagement. By investing in its community forest, L.A. County is not only enhancing the quality of life for its residents today but also ensuring a greener, healthier, and more resilient future for generations to come.
Clement Lau, DPPD, FAICP, is a Senior Analyst with the Los Angeles County Chief Sustainability Office. He was previously with the County’s Department of Parks and Recreation where he was the lead planner on data-driven, welcoming-focused parks needs assessments and master plans.
1. Community forest is defined as the collection of all trees in our communities, including along streets, between buildings, in parks, and around all of the places we live, work, and play.
2. CFMPs are sometimes referred to as Urban Forest Management Plans (UFMPs). L.A. County uses the term “community” rather than “urban” to reflect the diverse array of community types across the county, including urban, suburban, and rural.